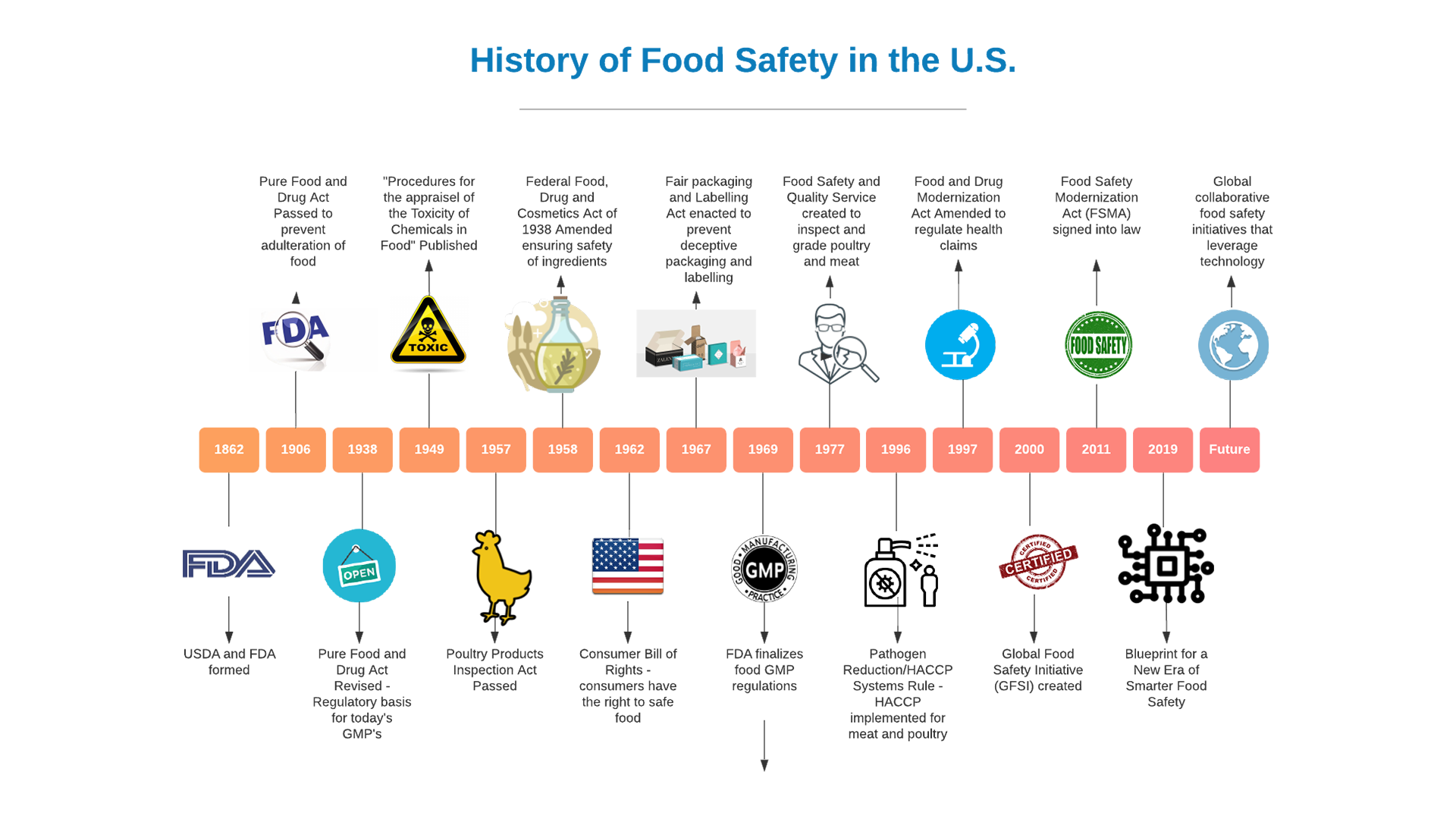
The saying “When America sneezes, the world catches a cold” could not be truer when it comes to food safety management. If we look at the history of food safety in the U.S., we can see how significant food safety regulatory events have impacted the rest of the world. From the creation of the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP’s), through the development of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) food safety systems and more recently the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), all have had a profound impact on way that food safety is viewed and managed throughout the world.
“What is the future of food safety?” many ask. The US FDA is moving into what they have described as the “New Era of Smarter Food Safety”. A new era that is sure to have a profound impact on the food safety around the world. According to the FDA this new blueprint is centered around four core elements:
- Tech-enabled Traceability, with the aim to leverage technology to achieve end-to-end traceability throughout the food supply chain.
- Smarter Tools and Approaches for Prevention and Outbreak Response, with the aim to enhance and strengthen root cause analysis and predictive analytics to help the industry modify current practices to avoid identified risks and provide more robust data.
- New Business Models and Retail Modernization. Looking at more traditional business models, the FDA is exploring the best ways to further modernize and help ensure the safety of foods sold at restaurants and other retail establishments.
- Food Safety Culture is a prerequisite to effective food safety management. The FDA believes that in order to make dramatic improvements in reducing the burden of foodborne disease that more needs to be done to influence the beliefs, attitudes, and, most importantly, the behaviours of people and the actions of organisations.
The FDA believes that these core elements will help create a safer and more digital, traceable food system for the future and that tech-enabled traceability is going to have a big impact on the global food supply chain.
Current status of traceability in the food supply chain
Traceability or product tracing is defined by the Codex Alimentarius Commission as “the ability to follow the movement of a food through specified stages of production, processing and distribution”. Traceability within food control systems is applied as a tool to control food hazards, provide reliable product information and guarantee product authenticity.
A typical food supply chain today is considered in theory to be linear from suppliers of raw agricultural commodities through producers and processors through distributors to retailers and finally consumers. However, the reality is a complex web of systems with interconnected networks of nodes and edges making up the value chain.